The fiber optic cable jackets play an important role in protecting fiber optic cables. Fiber optic cable jackets come in different materials for providing different protective functions. Fiber optic cable jackets can also be customized for indoor, outdoor, burial, or aerial applications. Understanding fiber cable jackets and fire ratings is essential for ensuring stable data transmission and safety. We’ll talk about this in this article.
Overview of Fiber Optic Cables
A fiber optic cable has an easy construction like the following picture including fiber core, cladding, coating, strength member, and outer jacket. The fiber core is to transmit signals. Covering the fiber core, the cladding layer protects the fiber core from light. The coating is simply a layer protecting the core and cladding from abrasion and water vapor. The strength member is a layer preventing the cable from breaking when stretched.
The outer cable jackets are designed to protect the fiber from exterior influence, including water, wind, sunlight, etc. The jackets are generally available in different colors, helping people recognize different types of fiber optic cables. For example, outdoor cable jackets are usually black against UV light.

Why Does Fiber Optic Cable Jacket Matter?
A fiber optic cable jacket is regarded as a safeguard for fiber optic cable. With the shielding of the cable jacket, the inner fiber can be protected from mechanical damage during and after installation. Besides, some cable jackets are designed for special environments with high temperatures or high corrosion. Different cable jackets have properties that make them apply to various scenarios.
Fiber Optic Cable Jacket Materials
When choosing the fiber optic cable jacket, jacket materials should be considered to meet the requirements of outdoor or indoor uses. There are some commonly used jacket materials: Polyethylene (PE), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Polyvinyl Difluoride (PVDF), and Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH). Let’s further explore them in the following content.
- PE
The PE fiber optic cable jackets are designed for outdoor applications. It provides excellent moisture, abrasion, and corrosion resistance. It features great electrical performance in a wide temperature range. It also has good chemical stability. A PE-made cable jacket with high mass density is hard while one with low mass density is flexible. These two types are called High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and both are the common cable jacket material. HDPE has better heat resistance and a high melting point while LDPE is the opposite.
- PVC
PVC is a cheap material with good mechanical properties and flame resistance. Affordability and accessibility make it a commonly used material. It has high electrical insulation and flexibility during installation. PVC cable jackets are preferred in indoor applications due to their instability in light and heat. But it will give off toxic gases, so it is not suitable for plenum applications.
- PVDF
PVDF is elastic and lightweight, featuring better flame resistance than PE jackets. It also has thermal conductivity, high chemical resistance, and heat resistance. PVDF can produce little smoke and is suitable for plenum cables and backbone applications.
- LSZH
As the name implies, Low Smoke Zero Halogen produces little smoke and no halogens when it burns. It has better flame resistance than PVC, suitable for poorly ventilated areas such as airplanes, subways, and tunnels. It is safe and environment-friendly, but it is one of the most expensive jacket materials.
Fiber Optic Cable Fire Ratings
According to NEC (National Electrical Code), fiber optical cable fire ratings are as follows, OFNP/OFCP, OFNR/OFCR, OFNG/OFCG, and OFN/OFC.
Each letter has its meaning. “OF” indicates optic fiber. “N” and “C” mean non-conductive or conductive. “R” and “P” are symbols of Riser and Plenum. “G” is General-Purpose. For example, OFNP is an optic fiber non-conductive plenum cable. The fire rating among riser, plenum, and general-purpose is P> R> G. A higher rating usually has wider applications than the lower one.
|
NEC Code |
Type |
Fire Resistance Levels
|
Applications
|
|
OFNP
|
Optic Fiber Non-conductive Plenum
|
1
|
Ventilation ducts, ducts, plenum or return air pressurization systems
|
|
OFCP
|
Optic Fiber Conductive Plenum
|
||
|
OFNR
|
Optic Fiber Non-conductive Riser
|
2
|
Vertical backbones
|
|
OFCR
|
Optic Fiber Conductive Riser
|
||
|
OFNG
|
Optic Fiber Non-conductive General-Purpose
|
3
|
General purpose, horizontal
|
|
OFCG
|
Optic Fiber Conductive General-Purpose
|
||
|
OFN
|
Optic Fiber Non-conductive
|
4
|
General purpose
|
|
OFC
|
Optic Fiber Conductive
|
OFNP vs OFNR
It's important to note that OFNP and OFNR cables have different specifications for Plenum and Riser applications. OFNP cables have the highest fire rating, and no other cables can be used in their place. They are highly fire-resistant and produce low levels of smoke. So, OFNP cables are generally used in plenum applications.
How To Choose the Right Cable Jacket?
We have mentioned some applications above. But how can you choose the right cable jacket in different scenarios? What factors should you consider? Your selection of cable jackets will vary based on your considerations.
Fire Ratings
Fiber optic cables with different fire ratings are used for different scenarios. OFNP is on the first fire rating, so the cable jacket made of plenum would be the first choice. The PVC cables can meet the fire rating of OFNR. LSZH cable jackets are on OFN fire rating. To ensure compliance with fire safety regulations, consider jackets made of PVC, or LSZH materials.
For different scenarios, you need to choose suitable fire ratings:
- For small buildings’ inner arrangement and in fire riser shafts in buildings of any type where risers are used, these 8 fire ratings are needed.
- In a fabricated duct and space for air circulation in a public building. For example, air conditioning piping or air routing ceiling: OFNP and OFCP are suitable.
- For vertical runs in a riser and riser-rated cable arrangement in a building like the corridors of buildings, elevator shafts, or wiring rooms spanning multiple floors: OFNP, OFCR, OFNR, OFCR.
Layout area
- Plenum Area: an area used for air circulation.
- Riser Area: A vertical ventilation shaft orplane between two floors in a building.
-
General-purpose Area: other areas that are not Plenum area or Riser area.
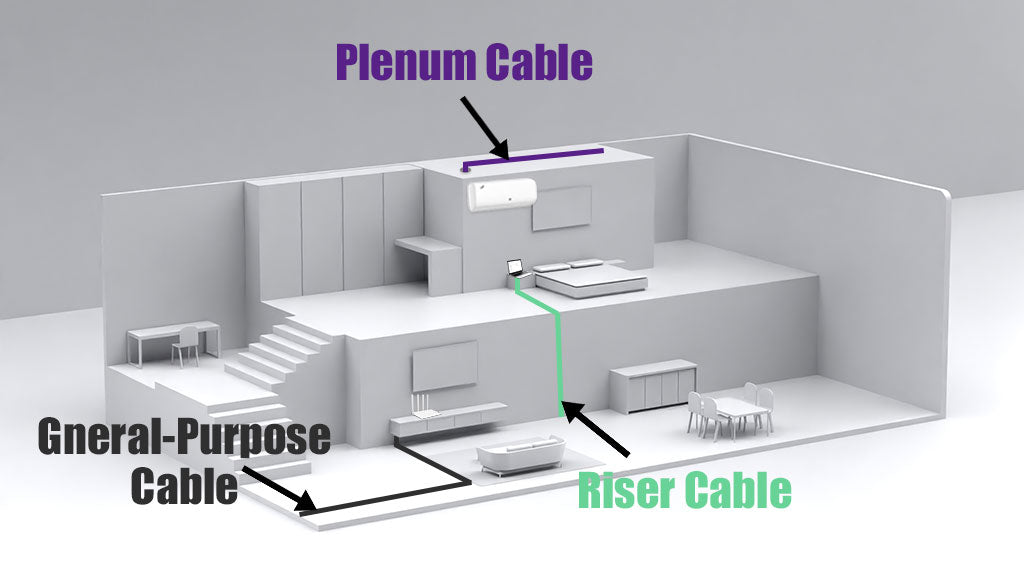
|
Plenum Area |
Riser Area |
General-purpose Area |
|
|
Plenum rated Cable |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
|
Riser Rated Cable |
❌ |
✅ |
✅ |
|
General-purpose Cable |
❌ |
❌ |
✅ |
Environment Conditions
Indoor and outdoor environments are quite different. Some fiber optic cable jackets are poor in corrosion resistance and high-temperature resistance, and such fiber optic cables are more suitable for indoor applications. If the cable jacket has good chemical resistance, water resistance, weather, and sun resistance, it will be more suitable for outdoors.
Conclusion
The right cable jacket provides with your safety and utility. However, it should be noted that jacket material is not the only factor for fire control. To prevent fire and ensure safety, you should also carefully plan your fiber optic cable route and other comprehensive measures.
FAQs
Does the cable jacket color relate to the performance or cable selection?
The cable jacket color has something to do with cable selection but has nothing to do with its performance. The cable jacket color helps you recognize the types of cable.
What’s the difference between the Plenum and Riser cable?
Their insulation is made of different materials. But the main difference is that the Plenum cable has a better fire rating than the Riser cable. In a plenum area, only Plenum cable is allowed.
How do you check the fiber optic cable material and fire rating?
For cables compliant with UL standards, Check the words on the fiber jacket that say the material and fire rating like “(UL) type PVC OFNR”.
For more information on this topic, you can keep up on our blogs. While VCELINK offers general and basic information for our customers and other visitors to the website, it’s not professional advice.


Be the first one to comment.
Leave a comment