Cables and wires are tightly related to transmit signals in the world of video, audio, and networks. Have you ever learned about the different constructions of these cables? While unshielded cables are commonplace in our daily use, the importance of physical protection cannot be overstated, especially in extreme environments where optimal performance is imperative.
Braided cables are often designed with various materials and styles to maximize cable performance. Some braided cables offer physical protection to reduce external damage, and some can protect data transmission from interference.
How well-acquainted are you with the nuances of braided cables? Do you know when to use these cables and what their benefits are? This blog embarks on a journey into the realm of braided cables and wires, revealing the constructions, applications, advantages, and so on.
What are Braided Cables?
In the 1800s, interference became a prevalent issue with the widespread adoption of electricity. People used to wrap the ground wires around conductors to reduce interference, but a new and more effective solution was needed for better cable performance. In the late 1800s, telephone engineers pioneered a breakthrough discovery: the wrapping tinsel wire around the conductors can effectively reduce radio interference. And this is the beginning history of braided cables.
Braided wires are the meshed shielding wrapped around the conductor. Available in various materials and styles, these braids offer versatile solutions tailored to diverse needs. For example, most braided wires are made of metal materials such as gold-plated and silver-plated copper for added interference protection. Additionally, alternatives like pure silver, pure nickel, and bronze are also utilized. The type of braiding materials can be affected by many factors, including the cable type, budget, and specific applications.
Necessity of Braided Cables
EMI is around people, from microwaves to smart devices, and braided cables are necessary to reduce EMI and RFI. A braided shielding cannot only reduce the interference of the cable but also ensure the transferred signal integrity, strength, and stability. A braided shielding can effectively prevent the cable from transmitting interference to nearby electrical devices, which is especially essential for environments full of different cables and connected equipment.
Moreover, the braided cable provides protection from external physical damage. The metallic mesh also offers added cable durability so that the cable can resist frequent bending and flexing. However, it should be noted that the braiding also makes the cable thicker, which increases the difficulty of cable installation.
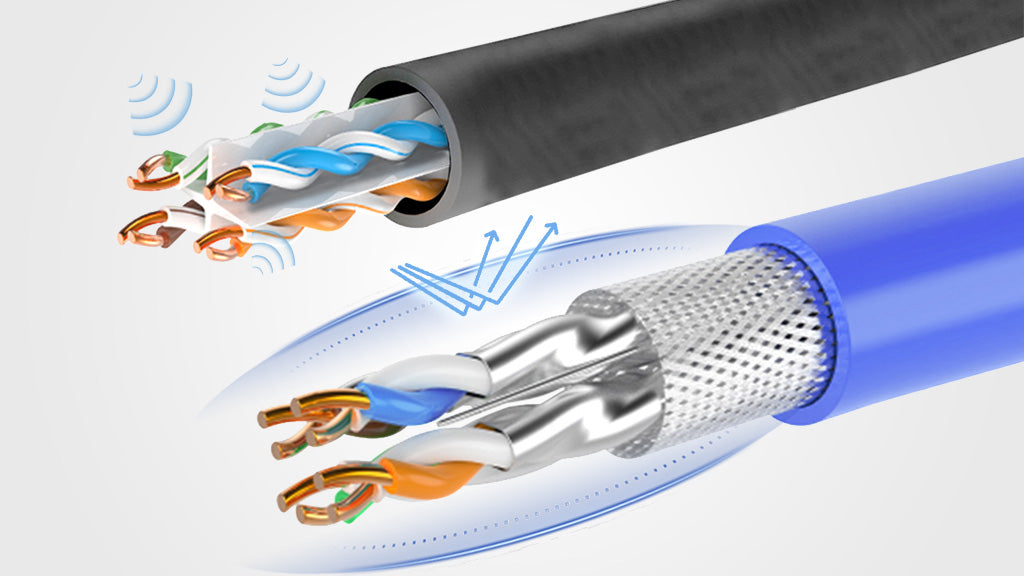
Notes: What is EMI?
EMI stands for Electromagnetic Interference. It refers to the disruption caused by external sources like unwanted signals and noise, which can negatively affect the signal quality and even cause data loss. EMI exists in all electrical devices, including electrical transmitters and household equipment.
Foil Shielding vs. Braided Shielding
Besides braided wires, foil shielding also helps reduce EMI and RFI. What are the similarities and differences between these two shielding methods? We’ll further explore it in the following content.
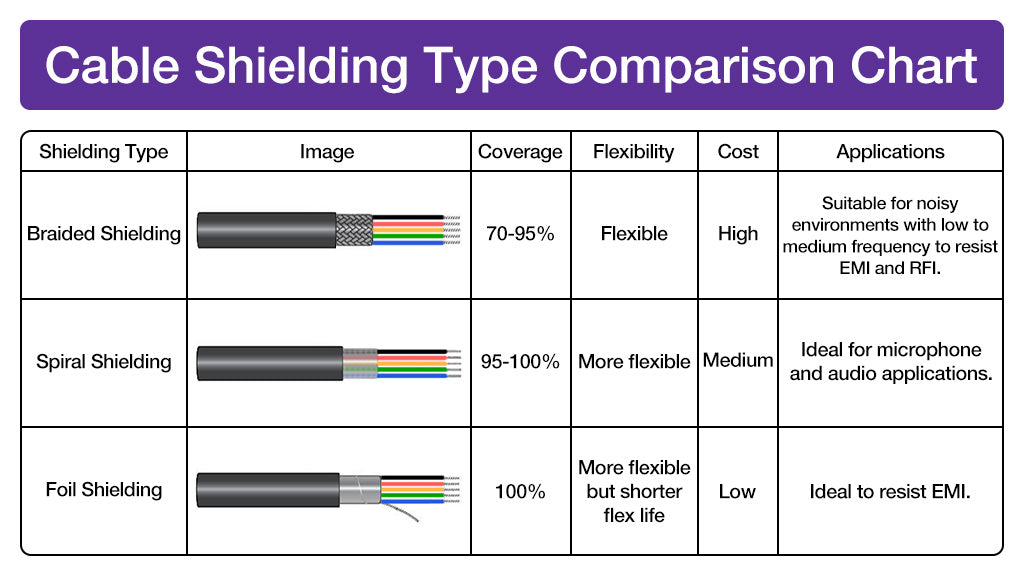
Compared to braided shielding, foil shielding has greater protection from interference but less costs. However, it is not as flexible as copper braided shielding and can be easier to tear or fold in some applications. Braided shielding can be more versatile to protect cables from outer damage and EMI.
Spiral Shielding vs. Braided Shielding
Spiral shielding is also one of the common cable shielding solutions. The strands of copper are wrapped parallel around the twisted pairs. Since the copper doesn’t need to be tangled, it can be less expensive, and has a larger cover area than braided shielding. While braided shielding can cover 70-90% of the area, spiral shielding can cover over 90% of the area. In addition, the spiral shielded cables can be easier to install and more flexible. But it is worth noting that this cable shielding solution has a gap in the shielding, which may cause interference to leak through the space. And it is more likely to damage than braided shielding.
Cable Shielding Type Comparison Chart
Here is a detailed comparison chart of braided, spiral, and foil aluminum shielding. Hope it will help you.
Where Can You Use Braided Wires?
Full coverage can be less practical in the electrical world, but a braided cable can offer 70%-95% coverage that can resist most external noise. So, where can braided cables be used? We list common applications for braided cables:
- Environments with frequent temperature changes
- Applications with high interferences
- High-vibration applications
- Environments with lots of connected devices
Guide for Effective Shielding
- Select a cable that can meet the specific requirements. You should consider factors such as environmental conditions, frequency of movement, and potential of interference. For instance, for environments that require frequent flexing and exposure to mechanical stress, braided cables offer superior durability over foiled cables as the foiled part can be easy to tear under such conditions.
- Ensure the cable has adequate shielding to reduce EMI and RFI. For environments with low or medium interference, the foil can be enough for protection. But for a more complex and noisier settings such as industrial or high density environments, the combination of foil and braid offer enhanced shielding effectiveness.
- Connectors are as important as cables in installation. Use connectors that can not only match the shielding performance of the cable but also ensure a secure and reliable connection. Pair braided cables with those connectors with metal housing for long-term reliability.
- Ensure the equipment and cables are correctly grounded to reduce unwanted noise and interference in the signal path.
Final Thoughts
Braided cables are reliable for resisting RMI and radio interference and offer added protection against external damage. These cables are common in the electrical and Ethernet world. For example, Cat7 and Cat8 Ethernet cables generally feature braided and foiled shielding for stable data transmission. Braided cables can still be the best choice in the future as technology continues to evolve and the demand for high-performance and reliable connectivity grows.
For more information on this topic, you can keep up on our blogs. While VCELINK offers general and basic information for our customers and other visitors to the website, it’s not professional advice.




Be the first one to comment.
Leave a comment